Biomedicine
 |
A defined in-vitro fermentation system to evaluate the impact of alterations of the intestinal microbiota (Iniciación 2013 – 2017)Studying the dynamics of the intestinal microbiome and its response to distinct environmental stimuli, such as dietary components, is complicated by the practical limitations of working with human volunteers. This project proposes modeling the microbiota in a fermenter, where culture conditions can be controlled, and determining composition through genomic and metabolomic techniques. |
 |
Brain-Computer InterfaceThe brain resulted through the evolution of complex motor-control, physiological, and metabolic processes. Detecting and interpreting the brain signals responsible for functional interactions with physical devises is the focus of this study led by Professor Ranganatha Sitaram. His research, financed by a FONDECYT project, aims to improve the quality of life for psychiatric and neurological patients through processes of neuromodulation and assisted self-regulation. |
 |
Regeneration of skin and engineering of tissuesBy introducing microalgae to a biocompatible polymeric matrix, Professor Tomás Egaña created a method helpful in regenerating skin damaged by abrasions and burns. This method takes advantage of the oxygen produced through the photosynthetic activity of microalgae, an antibacterial agent. This “green skin” will soon undergo clinical trials. |
 |
System for monitoring air flow and providing early accident alerts for tracheostomy patients (Copec-UC Foundation 2016 – 2018)Three-Way PhD Global Partnership Programme “Computational Mechanobiology and Bioengineering towards Biomaterial and Cell Therapies for Myocardial Infarction and Heart Failures (Foundation Dr. Leopold and Carmen Ellinger Stiftung, Germany 2015 – 2018) Functionalization and biocompatibility of magnetic nanorods: applications to cytoskeletal mechanical manipulation and stem cell differentiation (OPEN-UC Internacional Seed Funds 2017) |
 |
Magnetic resonance imaging technology for aging related diseases: brain, heart and vessels (Anillo de Investigación 2015 – 2018)Until recently, it was impossible to obtain high-resolution images in movement through nuclear magnetic resonance. Research led by Pablo Irarrázaval has allowed for unprecedented analyses of cardiac dynamics and functions. This scientific and diagnostic achievement was made possible through advanced magnetic-resonance image processing. |
 |
Improving reconstruction methods based on the acquisition of MRIs obtained for Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping (QSM) (FONDECYT Regular 2016 – 2019)QSM is a contrast technique for magnetic resonance images, with potential applications in detecting neurodegenerative diseases and brain microbleeds. This project deals with improving the underlying mathematical models and optimization methods used in QSM, the aims of which being to reduce noise/artifacts in the images, thereby increasing operative and diagnostic powers. |
 |
Free breathing 3D cardiac multiparametric magnetic resonance fingerprinting (FONDECYT Regular 2016 – 2019)This project is overseen by Professor Claudia Prieto. |
 |
Comprehensive evaluation of myocardial and coronary diseases using magnetic resonance imagining in 3D with auto-gating (FONDECYT Regular 2016 – 2019)Widening the use of magnetic resonance images for the diagnosis and monitoring of cardiac pathologies requires implementing movement-correcting and optimization techniques during the scanning procedure. The objective of this project is to implement a resonance-image navigator that aids in correcting respiratory movements in 2D and 3D. This navigator will also include magnetic resonance angiography, which will allow for detailed evaluations of cardiac anatomy and function. |
 |
The role of oxidative stress as a principal effector of toxicity in cigarette smoke. A novel approximation for developing bioactive filters for smokers (FONDECYT Regular 2016 – 2019)The disease and deaths associated with smoking are a significant public health concern, affecting millions of people worldwide. The pathogenicity of cigarette smoke is primarily measured through oxidative damage, which is not mitigated by common acetate filters. The development of new bioactive filters could positively impact the health of millions of smokers. |
 |
Quantitative radiology: Quantitative reports of total abdominal fat (FONDEF IdeA 2015 – 2017)The growing prevalence of obesity in the population underscores the need for quantitative methods of determining the percentage and distribution of body fat. The aim of this study is to develop models and algorithms for processing the separation of water and fat signals in magnetic resonance images that will provide reproducible quantitative parameters. These measurements can be applied towards improving the diagnosis and treatment of obese and overweight patients. |
 |
Evaluating the efficiency and objectivity of survey and feedback instruments for educational simulations of invasive procedures in health-related programs (VRI 2016 – 2018)The interdisciplinary development of instruments with objective evaluation measures for simulations of invasive medical procedures could relevantly contribute to the education of medical students and healthcare professionals; however, these instruments must be validated and evaluated in the clinical setting. |
 |
Pioneering model for vascular-trauma training through 3D printing based on images of real patients: an interdisciplinary initiative for simulations in surgical education (VRI 2016 – 2018)Training surgeons in repairing traumatic injuries in large veins and arteries is highly needed yet difficult to accomplish. An interdisciplinary team of doctors and engineers have created 3D-printed models in biomimetic resins that are based on computed tomography images of real patients. This advancement directly supports the training of vascular surgeons. |
 |
Biophysical characterization of structural rearrangement during native state switching in FKH1/FKH2 and RfaH transcription factors (FONDECYT Iniciación 2016 -2017)This project is overseen by Professor César Ramírez. |
 |
Use of domain information on image reconstruction procedures with applications to undersampled magnetic resonance imaging (FONDECYT Iniciación 2016 – 2019)This project is overseen by Professor Carlos Sing-Long. |
 |
Design of microbial consortia for the treatment of inflammatory diseases in the intestine (FONDEF IdeA 2017 – 2019)
This project is overseen by Professor Daniel Garrido. |
 |
Decoding individual brain states of sleep an memories from real-time pattern classification of simultaneous fMRI and EEG signals (FONDECYT Regular 2017)This project is overseen by Professor Ranganatha Sitaram. |
 |
Functionalization and biocompatibility of magnetic nanorods: applications to cytoskeletal mechanical manipulation and stem cell differentiation (OPEN-UC Internacional Seed Funds 2017)The interaction of magnetic nanorods with live cells is a growing area of interest due to possible applications in biomedicine. To increase the biocompatibility of these structures, research is being conducted regarding functionalization methodologies and on nanorod interactions with different cell types. |
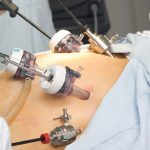 |
Effect of bariatric surgery on microbiota and its association with changes in bile acid homeostasis (FONDECYT 2015 – 2018)Bariatric surgery is an increasingly popular procedure in the treatment of morbid obesity. In collaboration with the Faculty of Medicine, research is being conducted on the effects of structural alterations in the gastrointestinal tract on the metabolism of bile salts and composition of the intestinal microbiota. |
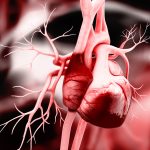 |
Three-way PhD Global Partnership Programme “Computational mechanobiology and bioengineering towards biomaterial and cell therapies for myocardial infarction and heart failures (Foundation Dr. Leopold and Carmen Ellinger Stiftung, Germany 2015 – 2018)This project is overseen by Professor Daniel Hurtado. |




 Español
Español
